A program is running automatically at regular intervals from cron, the time-based job scheduler. Look in /etc/cron.d/ for the configuration and see what command is being executed.
Here are the details which we have from the previous level:
- Host:
bandit.labs.overthewire.org - Port:
2220 - Username:
bandit21 - Password:
EeoULMCra2q0dSkYj561DX7s1CpBuOBt
So, The SSH syntax will be:
sshpass -p EeoULMCra2q0dSkYj561DX7s1CpBuOBt ssh [email protected] -p 2220
In this level, we need to find the password for the next level bandit22. The hint suggests that a program is running automatically at regular intervals using cron, the time-based job scheduler. So, Lets begin:
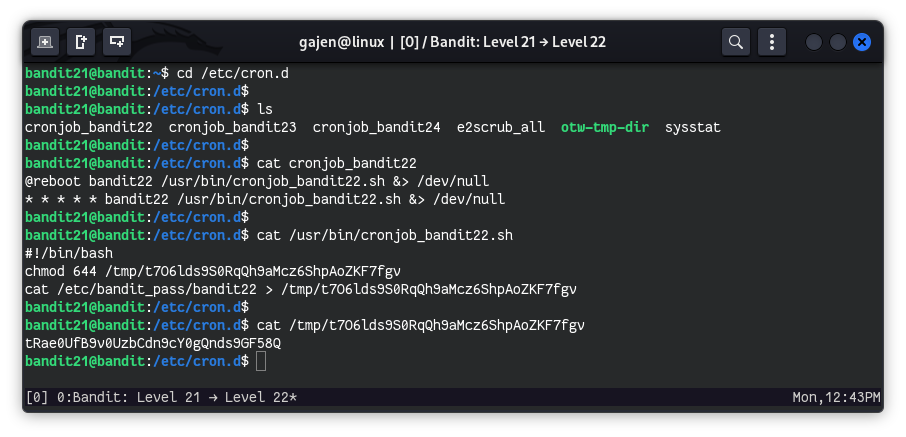
The cron jobs are usually stored in /etc/cron.d. We start by navigating to this directory.
cd /etc/cron.d
List the contents of /etc/cron.d to identify potential cron job files related to the next level.
ls
# Output:
# cronjob_bandit22 cronjob_bandit23 cronjob_bandit24 e2scrub_all otw-tmp-dir sysstat
Among these files, cronjob_bandit22 is of interest since it suggests a cron job for bandit22.
View the contents of cronjob_bandit22 to understand what commands are being executed by this cron job.
cat cronjob_bandit22
# Output:
# @reboot bandit22 /usr/bin/cronjob_bandit22.sh &> /dev/null
# * * * * * bandit22 /usr/bin/cronjob_bandit22.sh &> /dev/null
The file indicates that cronjob_bandit22.sh is executed by the bandit22 user at system reboot and every minute.
View the contents of /usr/bin/cronjob_bandit22.sh to see what it does.
cat /usr/bin/cronjob_bandit22.sh
# Output:
# #!/bin/bash
# chmod 644 /tmp/t7O6lds9S0RqQh9aMcz6ShpAoZKF7fgv
# cat /etc/bandit_pass/bandit22 > /tmp/t7O6lds9S0RqQh9aMcz6ShpAoZKF7fgv
The script changes the permissions of a file in /tmp and writes the contents of /etc/bandit_pass/bandit22 (the password for the next level) to this file.
Since the script writes the password to a file in /tmp, we can read this file to get the password for bandit22.
cat /tmp/t7O6lds9S0RqQh9aMcz6ShpAoZKF7fgv
# Output:
# tRae0UfB9v0UzbCdn9cY0gQnds9GF58Q