The password for the next level is stored in the file data.txt, which is a hexdump of a file that has been repeatedly compressed. For this level it may be useful to create a directory under /tmp in which you can work. Use mkdir with a hard to guess directory name. Or better, use the command “mktemp -d”. Then copy the datafile using cp, and rename it using mv (read the manpages!)
Here are the details which we have from the previous level:
- Host:
bandit.labs.overthewire.org - Port:
2220 - Username:
bandit12 - Password:
7x16WNeHIi5YkIhWsfFIqoognUTyj9Q4
So, The SSH syntax will be:
sshpass -p 7x16WNeHIi5YkIhWsfFIqoognUTyj9Q4 ssh [email protected] -p 2220
As we know from the hint, the password for the next level is stored in the file data.txt, which is encoded and compressed multiple times. So, Let begin:
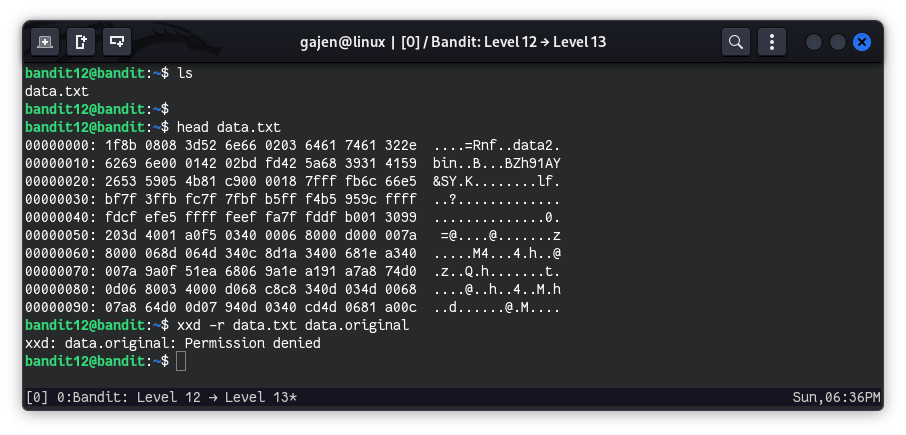
From data.txt file content, it seems like it contains the hex value of some type of file. So, first of all, we need to reverse the file from hex to its original form. But, I got a permission denied error, likely because we don’t have write privileges in our home directory. So, we’ll create a temporary directory in /tmp to accomplish our task.
Create a temporary directory in
/tmpand change to that directory:mkdir /tmp/data cd /tmp/dataReverse the hex back to the original file format:
xxd -r ~/data.txt data1Output of
ls -a:ls -a . .. data1Check the file type:
file data1 # Output: data1: gzip compressed data, was "data2.bin", last modified: Sun Jun 16 02:47:25 2024, max compression, from Unix, original size modulo 2^32 578Since the file is gzip compressed data, rename it with
.gzextension and unzip it:mv -v data1 data1.gz gunzip -d data1.gzOutput of
ls -a:ls -a . .. data1Check the file type again:
mv -v data1 data2 file data2 # Output: data2: bzip2 compressed data, block size = 900kSince the file is bzip2 compressed data, rename it with
.bz2extension and unzip it:mv -v data2 data2.bz2 bunzip2 data2.bz2Output of
ls -a:ls -a . .. data2Check the file type again:
mv -v data2 data3 file data3 # Output: data3: gzip compressed data, was "data4.bin", last modified: Sun Jun 16 02:47:25 2024, max compression, from Unix, original size modulo 2^32 20480Since the file is gzip compressed data again, rename it with
.gzextension and unzip it:mv -v data3 data3.gz gunzip -d data3.gzOutput of
ls -a:ls -a . .. data3Check the file type again:
mv -v data3 data4 file data4 # Output: data4: POSIX tar archive (GNU)Since the file is a tar archive, rename it with
.tarextension and extract it:mv -v data4 data4.tar tar -xvf data4.tarOutput of
ls -a:ls -a . .. data4.tar data5.binCheck the file type of the extracted file:
file data5.bin # Output: data5.bin: POSIX tar archive (GNU)Since the file is a tar archive again, rename it with
.tarextension and extract it:mv -v data5.bin data5.tar tar -xvf data5.tarOutput of
ls -a:ls -a . .. data4.tar data5.tar data6.binRemove the tar file and check the file type of the next extracted file:
rm -v data5.tar file data6.bin # Output: data6.bin: bzip2 compressed data, block size = 900kSince the file is bzip2 compressed data again, rename it with
.bz2extension and unzip it:mv -v data6.bin data6.bz2 bunzip2 data6.bz2Output of
ls -a:ls -a . .. data4.tar data6Check the file type again:
mv -v data6 data7 file data7 # Output: data7: POSIX tar archive (GNU)Since the file is a tar archive again, rename it with
.tarextension and extract it:mv -v data7 data7.tar tar -xvf data7.tarOutput of
ls -a:ls -a . .. data4.tar data7.tar data8.binCheck the file type of the next extracted file:
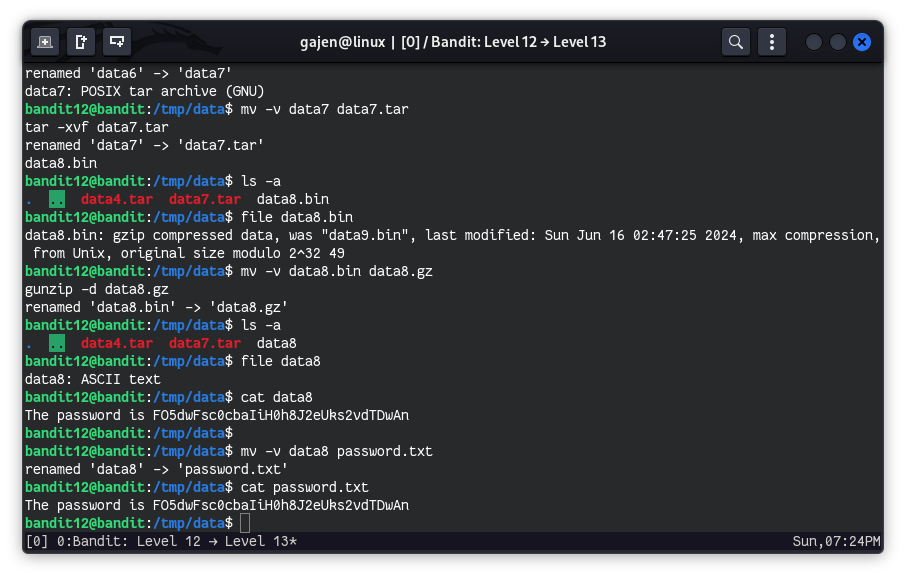
file data8.bin # Output: data8.bin: gzip compressed data, was "data9.bin", last modified: Sun Jun 16 02:47:25 2024, max compression, from Unix, original size modulo 2^32 49Since the file is gzip compressed data again, rename it with
.gzextension and unzip it:mv -v data8.bin data8.gz gunzip -d data8.gzOutput of
ls -a:ls -a . .. data4.tar data7.tar data8Check the file type again:
file data8 # Output: data8: ASCII textFinally, read the contents of the ASCII text file to get the password:
cat data8 # Output: The password is FO5dwFsc0cbaIiH0h8J2eUks2vdTDwAnOptional: Rename the file for clarity:
mv -v data8 password.txt cat password.txt # Output: The password is FO5dwFsc0cbaIiH0h8J2eUks2vdTDwAn